
News Directory
- I. Introduction
- II. The Ball Bearing Industry in China
- III. Types of Ball Bearings Produced in China
- IV. Materials Used in China Ball Bearing Manufacturing
- V. Quality Standards and Certifications
- VI. Future Trends in the Chinese Ball Bearing Market
- VII. Applications of China Ball Bearings
- VIII. Advantages of Sourcing Ball Bearings from China
- Conclusion
Navigating the World of China Ball Bearings: A Comprehensive Guide
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Ball Bearings
At its core, a ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races. Its primary function is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. Imagine two rings, an inner and an outer, with a set of perfectly spherical balls nestled between them. As one ring rotates, the balls roll, allowing for smooth, low-friction movement. This ingenious design minimizes the surface contact between moving parts, significantly reducing wear and tear, and enabling machinery to operate more efficiently and reliably.
B. Importance of Ball Bearings in Various Industries
Ball bearings are not just simple mechanical components; they are the unsung heroes of countless industries, acting as critical enablers of motion across the globe. From the smallest gadgets to the largest industrial machinery, their presence is ubiquitous. In the automotive industry, they ensure the smooth rotation of wheels, transmissions, and engines. In industrial machinery, they are vital for the efficient operation of motors, pumps, and conveyor systems. The precision and reliability offered by ball bearings are crucial for the high-speed, high-stress environments found in aerospace applications, while their compact size and smooth operation make them indispensable in consumer electronics and medical equipment. Essentially, any application requiring controlled rotational movement at varying speeds and loads likely relies on the fundamental technology of ball bearings to function effectively.
C. Overview of China as a Leading Manufacturer of Ball Bearings
Over the past few decades, China has emerged as a powerhouse in the global manufacturing landscape, and the ball bearing industry is no exception. What was once a nascent manufacturing sector has blossomed into a dominant force, driven by robust industrial policies, continuous investment in technology, and a vast, skilled workforce. Today, China stands as one of the world's leading producers and exporters of ball bearings, offering an extensive range of products from standard commodity bearings to highly specialized, custom-engineered solutions. This ascendancy is not merely about volume; it also reflects a significant improvement in manufacturing capabilities, quality control, and technological sophistication. For businesses worldwide, China represents a vital source for cost-effective, high-quality ball bearings, making it an essential consideration for global supply chains.
II. The Ball Bearing Industry in China
A. Historical Development
1. Early Manufacturing Practices
The origins of China's ball bearing industry can be traced back to the mid-20th century, largely spurred by the nation's drive towards industrialization. In its nascent stages, manufacturing practices were relatively rudimentary, often characterized by manual labor and less advanced machinery. The primary focus was on meeting domestic demand for basic industrial applications, with an emphasis on production volume rather than precision or advanced material science. Early bearing factories were largely state-owned, and their initial development was closely tied to national economic planning. Quality control mechanisms were still developing, and the industry faced significant challenges in terms of technological backwardness compared to established bearing manufacturers in Europe, North America, and Japan. However, this foundational period laid the groundwork, fostering a nascent understanding of bearing production processes and gradually building up a workforce with some level of expertise.
2. Growth in the Global Marketplace
The late 20th and early 21st centuries marked a pivotal transformation for China's ball bearing industry, fueled by economic reforms, opening up to the global market, and increased foreign investment. Chinese manufacturers began to acquire more advanced machinery, adopt international quality standards, and invest in research and development. The sheer scale of China's industrial base, coupled with competitive labor costs, allowed for rapid expansion in production capacity. This period saw a significant shift from solely domestic supply to becoming a major player in the global export market. Chinese ball bearings, initially perceived as lower-cost alternatives, began to gain wider acceptance as quality improved. The industry learned from international partners, absorbed new technologies, and gradually refined its manufacturing processes, positioning itself for global prominence.
B. Current Market Landscape
1. Major Manufacturers
Today, the Chinese ball bearing market is a dynamic and competitive landscape, comprising a mix of large state-owned enterprises, publicly listed companies, and a multitude of private manufacturers. While the market is highly fragmented, with numerous smaller players, several major manufacturers stand out due to their production scale, technological capabilities, and international presence. Companies such as ZWZ Group, HRB Bearing, and Luoyang LYC Bearing are among the traditional industry leaders, known for their comprehensive product ranges and significant domestic and international market share. In addition to these established giants, a growing number of agile and technologically advanced private companies are emerging, specializing in niche markets or high-precision bearings. This diverse manufacturing base ensures a wide spectrum of product offerings, catering to various quality and price points.
2. Export Statistics
China's ball bearing exports have seen phenomenal growth, solidifying its position as the world's largest exporter of bearings by volume. The country exports to virtually every corner of the globe, supplying industries from automotive and industrial machinery to consumer electronics and medical devices. While specific annual figures fluctuate, the overall trend points to a continuous increase in export value and quantity. This robust export performance is a testament to China's competitive pricing, massive production capacity, and improving product quality. The vast majority of these exports consist of standard ball bearings, but there's a growing trend towards exporting more specialized and higher-value-added products as Chinese manufacturers climb the technological ladder.
3. Key Industries Served
The versatility and widespread availability of China-produced ball bearings mean they serve a remarkably broad range of industries both domestically and internationally. Domestically, they are crucial for the country's massive manufacturing sector, including automotive production, heavy machinery, power generation, and railway transportation. On the global stage, Chinese ball bearings are integral components in:
Automotive Industry: Used in engines, transmissions, wheels, and various auxiliary systems.
Industrial Machinery: Essential for motors, pumps, gearboxes, machine tools, and manufacturing equipment.
Agricultural Machinery: Enabling the operation of tractors, harvesters, and other farm equipment.
Construction Equipment: Found in excavators, loaders, cranes, and other heavy-duty machinery.
Home Appliances: Integral to washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, and other consumer goods.
Power Tools: Ensuring smooth operation in drills, saws, and grinders.
Renewable Energy: Crucial for wind turbines and solar tracking systems.
Medical Equipment: Used in precision instruments and diagnostic machinery where reliability is paramount.
This extensive reach underscores the foundational role of Chinese ball bearings in supporting global industrial and technological development.

III. Types of Ball Bearings Produced in China
The vast manufacturing capabilities within China's ball bearing industry mean that virtually every standard and specialized type of ball bearing is produced, catering to a diverse array of industrial and consumer applications.
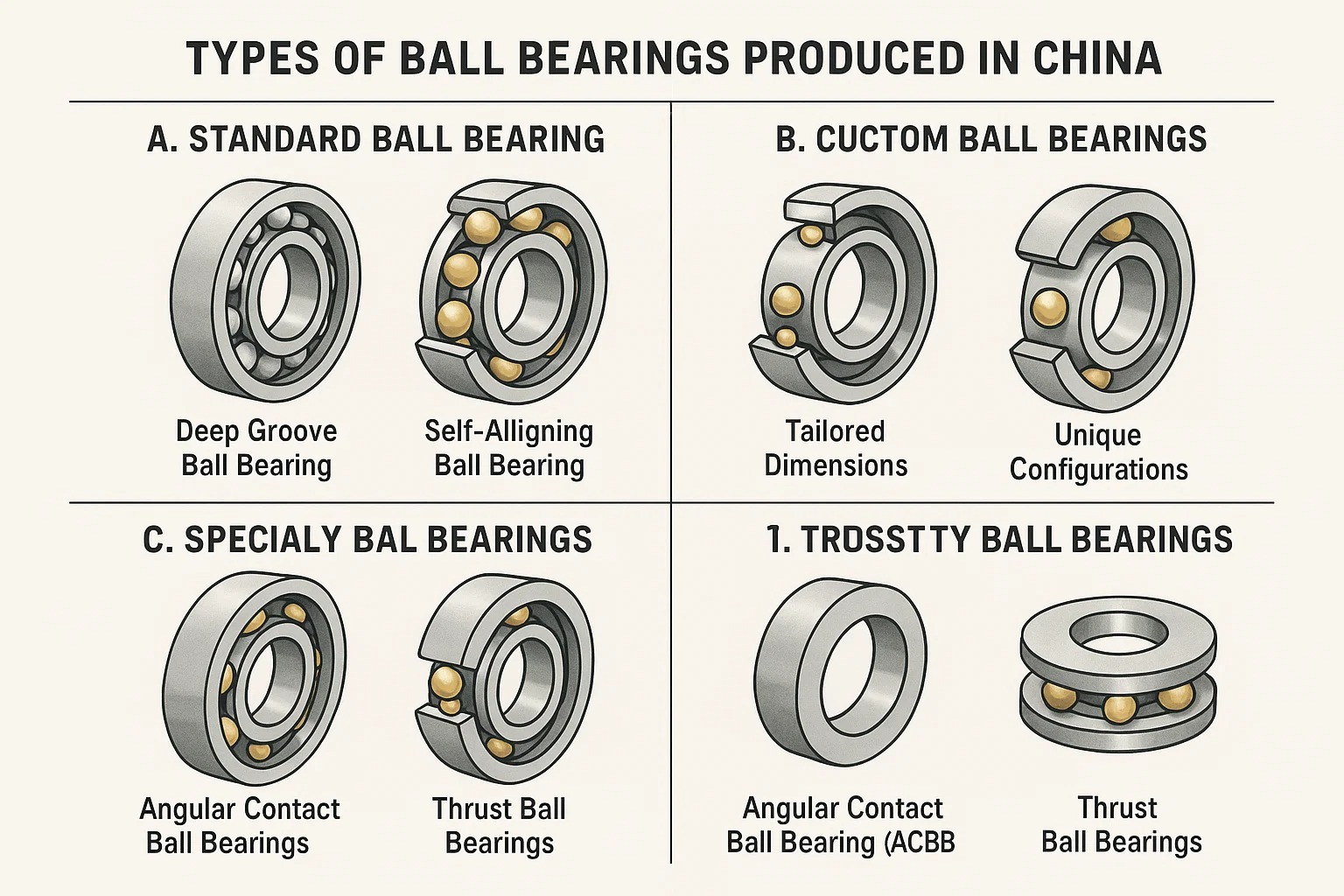
A. Standard Ball Bearings
Standard ball bearings form the bedrock of the industry, representing the most commonly manufactured and utilized types. These bearings are designed for general-purpose applications where moderate loads and speeds are encountered, and they are widely available in various sizes and configurations.
Deep Groove Ball Bearings (DGBBs): These are by far the most common type, characterized by deep raceway grooves that closely conform to the balls. This design allows them to handle both radial and moderate axial loads in both directions. Their versatility, high speed capability, and relatively low friction make them suitable for a myriad of applications, including electric motors, home appliances, automotive components, and general industrial machinery. Chinese manufacturers produce deep groove ball bearings in an extensive range of sizes, from miniature bearings for precision instruments to large bearings for heavy-duty industrial uses, often adhering to international standards like ISO and DIN.
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings (SABBs): Designed with two rows of balls and a common spherical raceway in the outer ring, self-aligning ball bearings are ideal for applications where misalignment between the shaft and housing might occur. They can compensate for angular misalignment up to a certain degree, making them suitable for environments where shaft deflection or mounting errors are anticipated. Common applications include agricultural machinery, textile machinery, and other systems where shaft flexibility is a factor. Chinese manufacturers offer these bearings in various series to meet different load and speed requirements.
B. Custom Ball Bearings
Beyond the standard offerings, Chinese manufacturers possess significant capabilities in producing custom ball bearings. This involves designing and manufacturing bearings to meet specific, often unique, application requirements that cannot be fulfilled by off-the-shelf solutions.
Tailored Dimensions and Tolerances: Custom bearings can be manufactured with non-standard bore diameters, outer diameters, widths, or specific tolerance classes to fit precise machinery designs. This is crucial for optimizing performance in highly sensitive equipment.
Special Materials and Coatings: While standard bearings use common bearing steels, custom applications might demand materials with enhanced properties for specific environments. This could include high-temperature alloys, corrosion-resistant stainless steels (beyond common grades), or even hybrid designs incorporating ceramic elements. Specialized coatings (e.g., for low friction, corrosion resistance, or electrical insulation) can also be applied.
Unique Configurations: This category includes bearings with integrated features, specialized seals, unconventional cage designs, or unique mounting provisions to simplify assembly or enhance functionality within a complex system. For example, a custom bearing might incorporate a sensor or a specialized mounting flange directly into its design.
Performance Optimization: Custom bearings are often developed to achieve specific performance targets, such as ultra-high speed capabilities, exceptionally low noise levels, extreme load capacity, or operation in vacuum environments. Chinese manufacturers, leveraging advanced design software and manufacturing processes, can work with clients to develop bespoke bearing solutions that precisely match their application's demands, offering a significant competitive advantage in specialized markets.
C. Specialty Ball Bearings
Chinese manufacturers also excel in the production of various specialty ball bearings, each engineered for specific operational conditions and load types.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings (ACBBs): These bearings have raceways that are offset relative to each other in the direction of the bearing axis, enabling them to accommodate significant combined radial and axial loads. They are commonly used in pairs or sets, face-to-face or back-to-back, to handle axial loads in both directions. Applications include machine tool spindles, gearboxes, pumps, and other high-precision machinery where rigidity and accurate shaft positioning are critical. China produces a wide range of angular contact ball bearings, including single row, double row, and matched pairs, in various contact angles.
Thrust Ball Bearings: Designed exclusively to handle axial loads, thrust ball bearings are not suitable for radial loads. They consist of two washers (raceways) and a cage with balls.
- Single Direction Thrust Ball Bearings: Can only handle axial loads in one direction.
- Double Direction Thrust Ball Bearings: Can handle axial loads in both directions. They are commonly found in applications like rotating tables, crane hooks, and automotive steering systems, where axial forces need to be supported. Chinese production includes both single and double direction configurations, in various sizes.
Miniature and Instrument Ball Bearings: These are extremely small bearings designed for precision applications where space is limited and high accuracy is required. They are crucial components in medical devices, dental equipment, robotics, computer peripherals, and other high-tech instruments. Chinese manufacturers have developed sophisticated production lines for these delicate bearings, ensuring high precision and smooth operation.
Thin Section Ball Bearings: Characterized by very small cross-sections relative to their bore diameter, these bearings offer space and weight savings while maintaining performance. They are ideal for applications where compact design is critical, such as robotics, aerospace components, and optical equipment. China's production in this area includes various types like radial, angular contact, and four-point contact designs.
Non-Standard and Hybrid Bearings: This broad category includes bearings designed for specific environments like high temperatures (e.g., using ceramic balls or specialized lubricants), corrosive environments, or applications requiring electrical insulation. Hybrid bearings, incorporating ceramic balls with steel rings, offer advantages like higher speeds, longer life, and reduced friction. Chinese manufacturers are increasingly investing in the production of these advanced and specialized bearing types to meet the evolving demands of modern industries.
IV. Materials Used in China Ball Bearing Manufacturing
The performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of a ball bearing are fundamentally determined by the materials used in its construction. Chinese ball bearing manufacturers utilize a range of high-quality materials, each selected for specific properties to meet diverse application requirements.
Chrome Steel (AISI 52100)
Composition and Properties: Chrome steel, specifically AISI 52100 (also known as 100Cr6 in Europe or GCr15 in China), is the most common and widely used material for ball bearing rings and balls. It is a high-carbon chromium alloy steel known for its exceptional hardness (typically HRC 60-65 after heat treatment), high wear resistance, and good fatigue strength. The chromium content provides good hardenability and contributes to its wear resistance.
Advantages: Its excellent balance of hardness, wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness makes it suitable for the vast majority of bearing applications where high loads and speeds are encountered under normal operating conditions. It offers good dimensional stability and a long service life when properly lubricated and maintained.
Applications: Widely used in standard deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, and other general industrial and automotive bearings. It is the go-to material for applications not exposed to extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, or electrical conductivity issues.
Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316, 440C)
Composition and Properties: Stainless steels are chosen for applications requiring corrosion resistance.
- AISI 440C: This is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel with good hardness (HRC 58-60 after heat treatment) and excellent corrosion resistance compared to chrome steel. It contains a higher percentage of chromium (typically 16-18%) and some molybdenum, enhancing its resistance to rust and pitting.
- AISI 304 and 316: These are austenitic stainless steels. AISI 304 (18/8 stainless steel) offers good general corrosion resistance. AISI 316 contains molybdenum, which significantly improves its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich environments. While they offer superior corrosion resistance, their hardness is lower than 440C, making them more suitable for lighter loads or specific applications where corrosion is the primary concern over extreme wear.
Advantages: Superior corrosion resistance in humid, wet, or mildly acidic/alkaline environments. 440C also offers good hardness and wear resistance in corrosive conditions.
Applications: Widely used in medical equipment, food processing machinery, marine applications, chemical processing, and cleanroom environments where hygiene and resistance to corrosive media are paramount. Bearings in these materials are also critical in applications exposed to moisture or outdoor elements.
Ceramic (Silicon Nitride, Zirconia)
Composition and Properties: Ceramic bearings typically use rolling elements (balls) made from ceramic materials, most commonly Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) or Zirconia (ZrO2), combined with steel or ceramic rings.
- Silicon Nitride (Si3N4): Known for its exceptional hardness, high strength, low density, excellent thermal shock resistance, and non-magnetic properties. It is also an electrical insulator.
- Zirconia (ZrO2): Offers good toughness, lower hardness than Silicon Nitride, and better resistance to certain chemicals.
Advantages:
- Higher Speeds: Lower density leads to less centrifugal force, allowing for significantly higher rotational speeds.
- Longer Life: Reduced friction and wear, combined with higher hardness, contribute to extended bearing life, especially in high-speed or poor lubrication conditions.
- Corrosion Resistance: Ceramics are highly resistant to most corrosive substances.
- Electrical Insulation: Prevents current passage, crucial in applications with stray electrical currents.
- High Temperature Capability: Can operate at much higher temperatures than steel bearings.
- Reduced Lubrication Needs: Lower friction can sometimes allow for minimal or even "dry" operation.
Applications: High-speed spindles in machine tools, aerospace applications, electric motors (to prevent electrical erosion), vacuum environments, medical and dental instruments, and specific automotive applications where weight reduction and high performance are critical. Often used in hybrid bearings (steel rings with ceramic balls).
Plastic (for specific applications)
Composition and Properties: Bearings made from various types of plastic, such as acetal (POM), nylon, PTFE (Teflon), or PEEK, often incorporate glass or carbon fibers for enhanced strength. They typically feature stainless steel or glass balls.
Advantages:
- Corrosion-Free: Completely resistant to rust and many chemicals.
- Lightweight: Significantly lighter than metal bearings.
- Self-Lubricating: Many plastic bearings are designed to operate without external lubrication.
- Non-Magnetic/Non-Conductive: Useful in specific electrical or magnetic sensitive environments.
- Quiet Operation: Inherently quieter than metal bearings.
Limitations: Generally have lower load capacity, lower speed limits, and poorer dimensional stability compared to metal bearings, and are limited by temperature ranges.
Applications: Ideal for applications where corrosion resistance, non-magnetic properties, or a lubricant-free environment are critical, and where loads and speeds are relatively low. Examples include food and beverage processing, marine environments, medical devices (non-MRI), textile machinery, and some consumer goods.
Chinese manufacturers carefully select and process these materials, employing advanced heat treatment, surface finishing, and quality control techniques to ensure that the final ball bearings meet the stringent performance and reliability demands of diverse industries.

V. Quality Standards and Certifications
When sourcing ball bearings from China, understanding the quality standards and certifications is paramount. It ensures that the products meet performance expectations, comply with regulatory requirements, and ultimately contribute to the reliability and longevity of your equipment. Chinese manufacturers have made significant strides in adopting and adhering to international quality benchmarks.
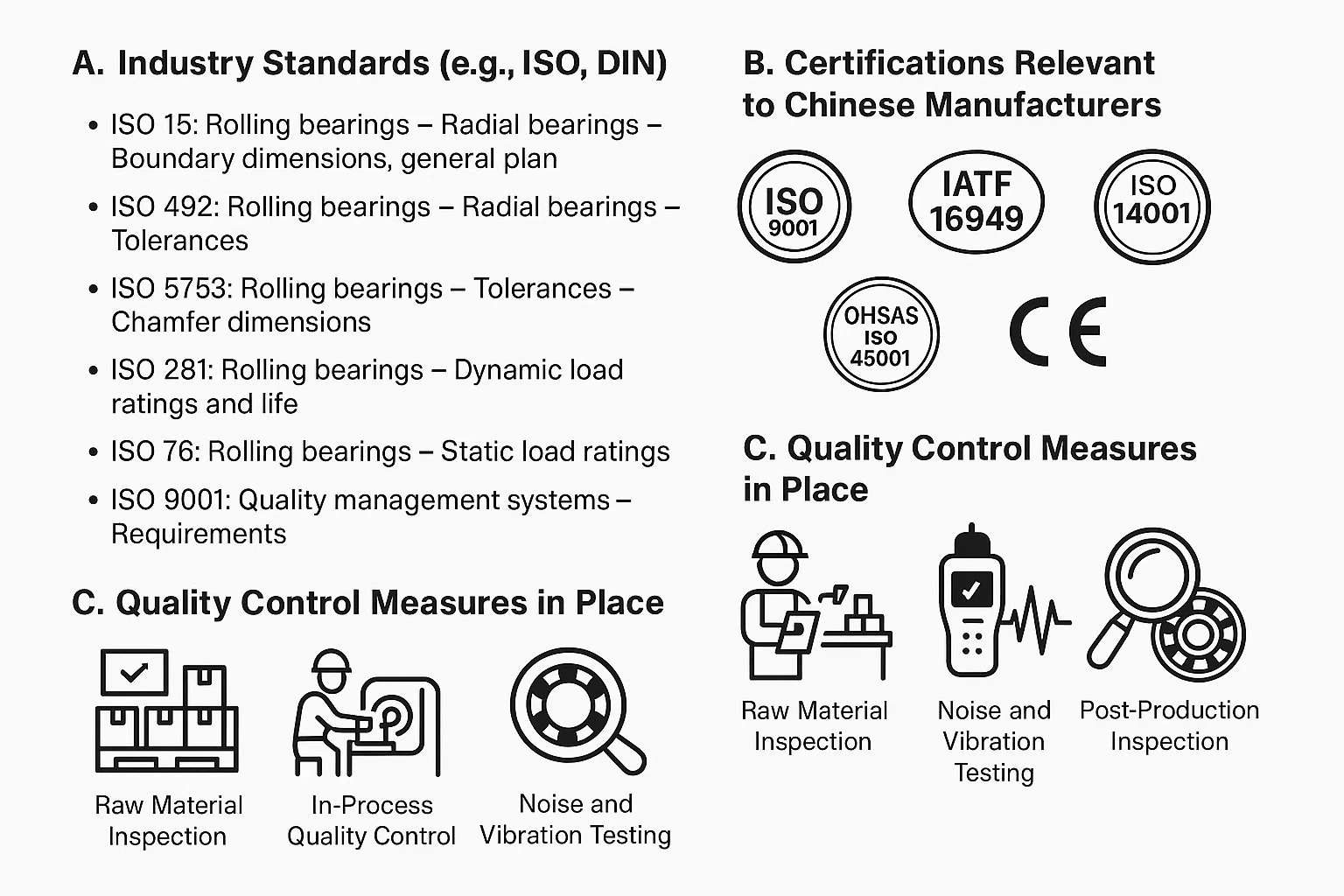
A. Industry Standards (e.g., ISO, DIN)
The global ball bearing industry operates under a framework of rigorous international standards, which define dimensions, tolerances, materials, testing methods, and performance criteria. Reputable Chinese manufacturers rigorously adhere to these standards to ensure interchangeability, consistent quality, and global acceptance of their products.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO standards are the most widely recognized and accepted global benchmarks for quality management systems and product specifications. For ball bearings, key ISO standards include:
- ISO 15: Rolling bearings – Radial bearings – Boundary dimensions, general plan: Defines the general dimensions for radial rolling bearings, allowing for interchangeability between manufacturers.
- ISO 492: Rolling bearings – Radial bearings – Tolerances: Specifies the dimensional and running accuracy tolerances for radial rolling bearings.
- ISO 5753: Rolling bearings – Tolerances – Chamfer dimensions: Outlines the specifications for chamfer dimensions.
- ISO 281: Rolling bearings – Dynamic load ratings and life: Provides methods for calculating the basic dynamic load rating and basic rating life of rolling bearings.
- ISO 76: Rolling bearings – Static load ratings: Defines the basic static load rating and static equivalent load for rolling bearings.
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems – Requirements: This is a crucial standard for the manufacturing process itself. It ensures that a manufacturer has a robust quality management system in place, covering everything from design and production to inspection and delivery. Many leading Chinese bearing manufacturers are ISO 9001 certified, indicating a commitment to consistent quality processes.
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung - German Institute for Standardization): While ISO is international, DIN standards are widely respected and often used in conjunction with or even precede ISO standards in the bearing industry, particularly for European markets. Many Chinese manufacturers, especially those exporting to Europe, ensure compliance with relevant DIN norms for dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications. Examples include DIN 625 (for deep groove ball bearings) and DIN 620 (for tolerances of rolling bearings). Adherence to DIN standards often signifies a higher level of precision and quality control.
B. Certifications Relevant to Chinese Manufacturers
Beyond product-specific standards, several certifications demonstrate a Chinese manufacturer's commitment to quality, environmental responsibility, and specific industry requirements.
ISO 9001 (Quality Management System): As mentioned, this is fundamental. An ISO 9001 certified manufacturer has established and maintains a quality management system that ensures products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. This certification is a strong indicator of a well-organized and quality-focused operation.
IATF 16949 (Automotive Quality Management System): For manufacturers supplying to the automotive industry, IATF 16949 is a highly critical and more stringent quality management system standard built upon ISO 9001. It includes specific requirements for the automotive sector, focusing on defect prevention and continuous improvement. Many Chinese bearing suppliers to global automotive OEMs hold this certification, signifying their capability to meet the demanding quality levels required by the automotive sector.
ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System): This certification demonstrates a manufacturer's commitment to minimizing its environmental impact and complying with environmental regulations. While not directly related to bearing performance, it reflects a responsible and sustainable business practice, which is increasingly important for international buyers.
OHSAS 18001 / ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety): These certifications indicate a robust occupational health and safety management system. They ensure a safe working environment for employees, which can indirectly reflect on product quality through consistent and stable production processes.
CE Marking (Conformité Européenne): While not a quality standard per se, the CE mark indicates that a product complies with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For bearings used in machinery destined for the EU market, this compliance is often necessary.
C. Quality Control Measures in Place
Reputable Chinese ball bearing manufacturers implement multi-layered quality control measures throughout the entire production process, from raw material sourcing to final product inspection.
Raw Material Inspection: Incoming raw materials (steel rods, tubes, cages, seals) are rigorously inspected for chemical composition, hardness, metallurgical defects, and dimensional accuracy. Only materials meeting strict specifications are accepted for production.
In-Process Quality Control: At every stage of manufacturing – including forging, turning, heat treatment, grinding, honing, and assembly – critical parameters are monitored. This involves:
- Dimensional Checks: Using precision measuring equipment (micrometers, calipers, CMMs - Coordinate Measuring Machines) to ensure components adhere to tight tolerances.
- Surface Finish Analysis: Measuring the roughness and integrity of raceway surfaces, which directly impacts bearing life and noise.
- Hardness Testing: Verifying that heat treatment processes have achieved the desired hardness levels for rings and rolling elements.
- Roundness and Runout Checks: Ensuring the geometric precision of the bearing components to minimize vibration and noise.
Post-Production Inspection:
- Noise and Vibration Testing: Bearings are often tested on specialized equipment to detect abnormal noise or vibration levels, indicating potential defects.
- Life Testing: While not every bearing is life-tested, samples are put through accelerated fatigue tests to validate design and material integrity.
- Appearance Inspection: Visual checks for surface defects, corrosion, proper lubrication, and accurate marking.
- Packaging Inspection: Ensuring proper packaging to prevent damage during transit and storage.
Traceability: Many manufacturers implement robust traceability systems, allowing them to track specific batches of raw materials, production dates, and inspection results for each bearing or batch of bearings. This is crucial for accountability and problem-solving if issues arise.
Continuous Improvement: A commitment to quality often includes lean manufacturing principles, Six Sigma methodologies, and regular audits (internal and external) to identify areas for improvement and maintain high standards over time.
By understanding and verifying these standards, certifications, and quality control processes, buyers can make informed decisions and confidently source high-quality ball bearings from China.
VI. Future Trends in the Chinese Ball Bearing Market
The Chinese ball bearing industry is not static; it is a dynamic sector constantly evolving to meet global demands, embrace technological advancements, and respond to environmental pressures. Several key trends are shaping its future trajectory, indicating a shift towards higher value-added products and more sophisticated manufacturing.
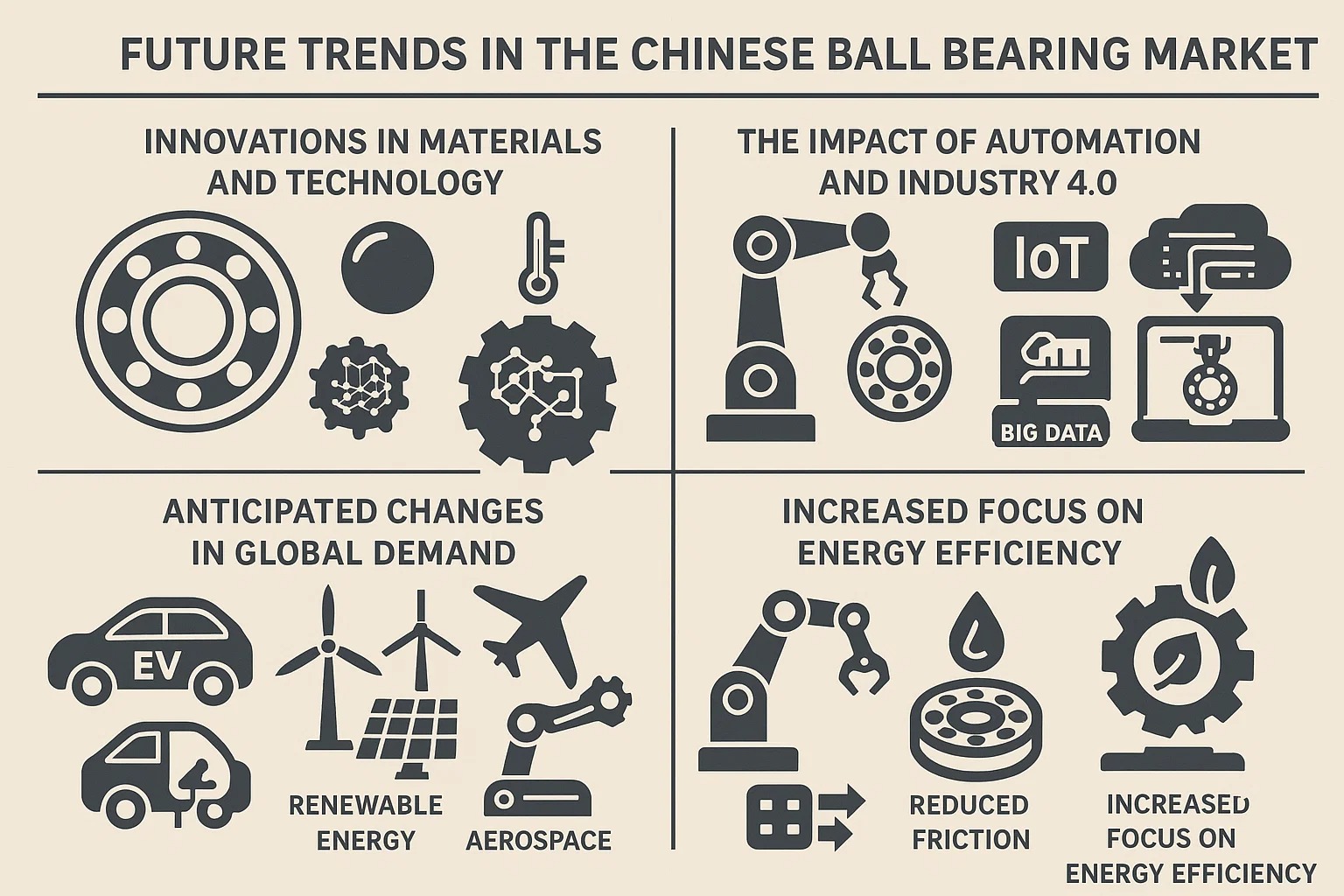
A. Innovations in Materials and Technology
The future of Chinese ball bearing manufacturing is deeply intertwined with advancements in materials science and innovative technological applications.
Advanced Materials:
- High-Performance Steels: Beyond standard chrome steel, there's a growing emphasis on developing and utilizing advanced high-purity bearing steels with improved fatigue life, higher load capacities, and better resistance to specific environmental conditions (e.g., higher temperatures or corrosive agents). This includes vacuum-degassed steels and electro-slag remelting (ESR) steels.
- Hybrid Bearings and Full Ceramics: The adoption of hybrid bearings (steel rings with ceramic balls) and full ceramic bearings is expected to grow significantly. As discussed, these materials offer superior properties such as electrical insulation, lower weight, higher speed capabilities, better corrosion resistance, and reduced lubrication requirements. Demand from industries like electric vehicles, aerospace, and high-speed machinery will drive this trend.
- Specialty Coatings and Surface Treatments: Research and development are focused on applying advanced coatings (e.g., DLC - Diamond-Like Carbon, TiN - Titanium Nitride) to bearing components. These coatings enhance surface hardness, reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and provide electrical insulation, extending bearing life and performance in challenging conditions.
Nanotechnology Integration: The application of nanotechnology is a burgeoning area. This includes developing lubricants with nano-additives to improve lubrication efficacy, creating surfaces with nano-scale textures to reduce friction, and potentially incorporating nanomaterials into bearing components for enhanced strength and durability.
Smart Bearings (Integrated Sensors): A major technological leap is the development of "smart bearings" with integrated sensors. These bearings can monitor critical operational parameters in real-time, such as:
- Temperature: Preventing overheating and catastrophic failure.
- Vibration: Detecting early signs of wear or damage.
- Speed and Load: Providing precise operational data. This data enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, optimizing performance, and improving overall system reliability. Chinese manufacturers are actively investing in R&D to embed these capabilities.
Improved Lubrication Solutions: Innovations in lubrication are crucial for bearing longevity. This includes the development of advanced synthetic lubricants, solid lubricants for extreme conditions, and improved sealing technologies to retain lubricants and prevent contamination.
B. The Impact of Automation and Industry 4.0
The Chinese bearing industry is increasingly embracing automation and the principles of Industry 4.0 to enhance efficiency, precision, and competitiveness.
Automated Production Lines: The shift from labor-intensive processes to highly automated manufacturing lines is accelerating. This includes robotic handling of components, automated grinding and honing machines with in-process gauging, and automated assembly. Automation reduces human error, improves consistency, and increases production speed and volume.
IoT (Internet of Things) and Connectivity: Integration of IoT devices across the manufacturing floor allows for real-time data collection from machines and processes. This data is then used for monitoring, analysis, and optimization of production parameters.
Big Data Analytics and AI (Artificial Intelligence): The vast amounts of data collected from automated lines are being analyzed using big data tools and AI algorithms. This enables:
- Predictive Maintenance of Manufacturing Equipment: Reducing machine downtime.
- Process Optimization: Identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement in manufacturing processes.
- Quality Prediction: Anticipating and preventing defects before they occur, leading to higher first-pass yield rates.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Improving logistics and inventory management.
Digital Twins: The creation of digital twins – virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems – is gaining traction. This allows manufacturers to simulate and test different scenarios in a virtual environment before implementing them in the real world, optimizing design, production, and performance.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): While not yet mainstream for main bearing components, additive manufacturing is being explored for prototypes, specialized cages, and customized tooling. This offers flexibility and the ability to produce complex geometries not easily achievable with traditional methods.
These advancements in automation and Industry 4.0 are allowing Chinese manufacturers to move up the value chain, producing bearings with higher precision, better quality, and greater consistency, while also optimizing operational costs.
C. Anticipated Changes in Global Demand
The global demand for ball bearings is constantly evolving, influenced by macroeconomic factors, technological shifts, and emerging industries. Chinese manufacturers are positioning themselves to capitalize on these changes.
Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs): The rapid expansion of the EV market is a significant driver. EVs require specialized bearings that can withstand higher speeds, operate more quietly, and are often electrically insulated. Chinese manufacturers are heavily investing in R&D and production capabilities for EV-specific bearings.
Renewable Energy Sector Expansion: The growth of wind energy (wind turbines) and solar energy (solar tracking systems) drives demand for large, robust, and often customized bearings designed for harsh outdoor conditions and long service life.
Aerospace and Defense: As China's aerospace and defense industries grow, so does the demand for high-precision, high-reliability, and lightweight bearings that meet stringent safety and performance standards. This also pushes for innovation in materials and manufacturing processes.
Robotics and Automation: The global surge in automation and robotics requires compact, precise, and high-performance bearings. Chinese manufacturers are adapting their product lines to cater to the specific needs of these rapidly advancing fields.
Industry Upgrades in Developing Economies: As developing economies industrialize, there will be a continued strong demand for standard and cost-effective ball bearings, a segment where China remains highly competitive.
Increased Focus on Energy Efficiency: Global regulations and market demands are pushing for more energy-efficient machinery. This translates to a demand for bearings with lower friction, improved seals, and optimized designs that contribute to overall energy savings.
These trends indicate that the Chinese ball bearing market is moving towards greater sophistication, higher performance, and a more strategic alignment with global industrial and technological megatrends, solidifying its position as a critical player in the international bearing supply chain.
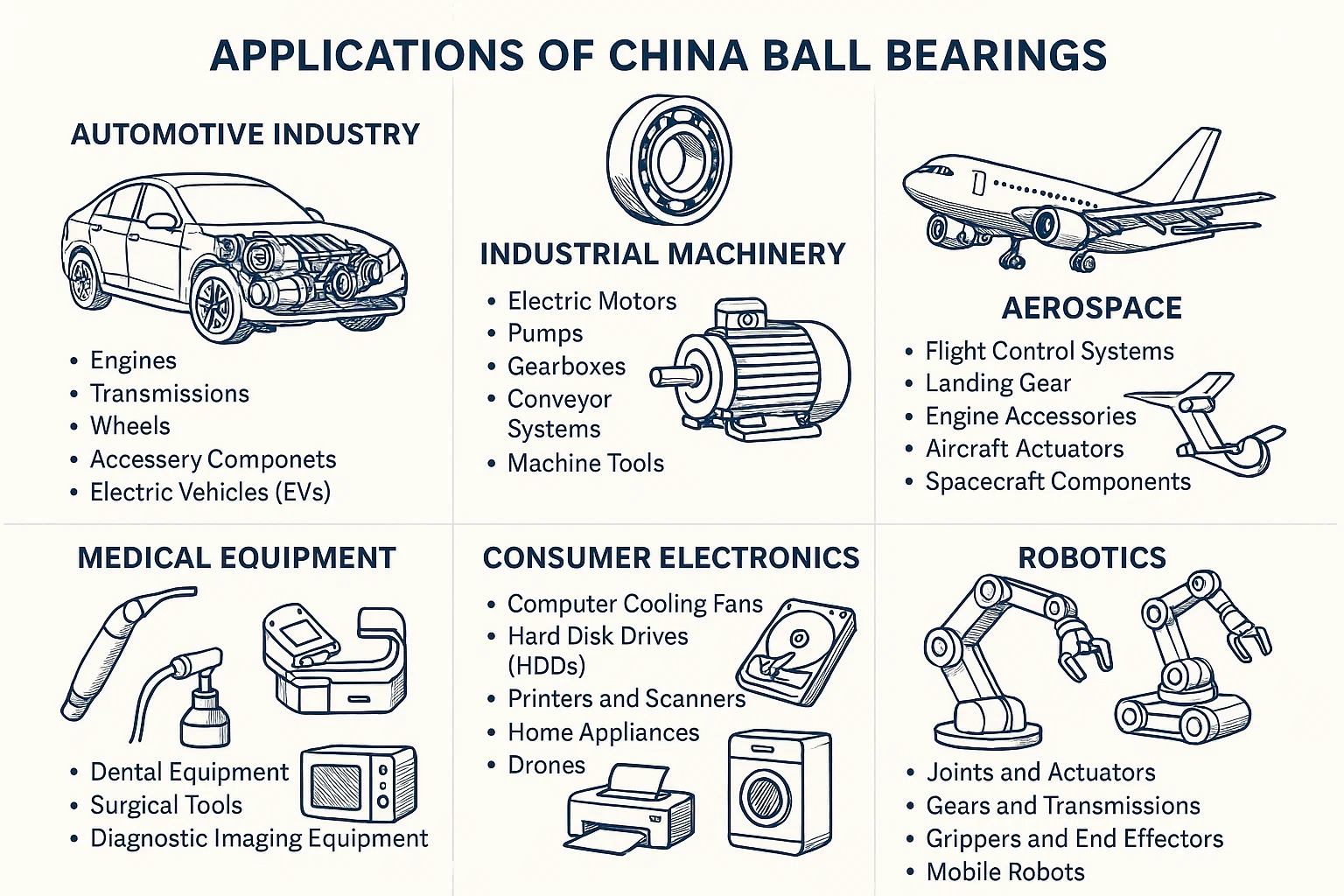
VII. Applications of China Ball Bearings
The ubiquity of ball bearings means they are integral components in virtually every sector that involves rotational motion. Chinese manufacturers supply an enormous volume and variety of ball bearings that find critical applications across a vast spectrum of industries, powering everything from our daily appliances to advanced industrial machinery and aerospace systems.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is one of the largest consumers of ball bearings, and Chinese-made bearings play a crucial role in vehicles worldwide. They are essential for:
- Engines: Supporting rotating shafts like crankshafts and camshafts, reducing friction, and ensuring smooth operation.
- Transmissions (Manual and Automatic): Facilitating the smooth rotation of gears and shafts, crucial for power transfer and gear shifting.
- Wheels: Wheel bearings are fundamental for the free rotation of a vehicle's wheels, supporting the vehicle's weight and handling radial and axial loads.
- Accessory Components: Found in alternators, water pumps, air conditioning compressors, power steering pumps, and electric cooling fans, ensuring their efficient and reliable operation.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): With the shift to EVs, new demands arise for high-speed, low-noise, and electrically insulated bearings in electric motors, drivetrains, and associated systems. Chinese manufacturers are rapidly developing specialized bearings for this growing segment.
Industrial Machinery
Industrial machinery, spanning manufacturing, construction, mining, and agriculture, relies heavily on ball bearings for its operation.
- Electric Motors: Bearings are fundamental to the operation of nearly all electric motors, supporting the rotor shaft and allowing for efficient, low-friction rotation.
- Pumps: Used in various types of pumps (centrifugal, positive displacement) for water, oil, and chemicals, ensuring stable shaft rotation and sealing.
- Gearboxes: Facilitating the smooth and efficient transfer of power within reduction units and speed increasers.
- Conveyor Systems: Supporting rollers and idlers in material handling systems, enabling continuous movement of goods.
- Machine Tools: Crucial for precision and stability in lathes, milling machines, grinders, and drilling machines, especially in spindles where high accuracy and rigidity are paramount.
- Textile Machinery: Enabling the high-speed and precise movements required in weaving, spinning, and knitting equipment.
- Agricultural Equipment: Found in tractors, harvesters, seeders, and irrigation systems, providing robustness for demanding outdoor conditions.
Aerospace
While the aerospace industry demands extremely high precision and reliability, Chinese manufacturers are increasingly contributing to this sector, particularly for general aviation and specific aircraft systems. Bearings here must withstand extreme temperatures, high speeds, and significant loads, often with stringent weight limitations. Applications include:
- Flight Control Systems: Ensuring smooth and precise movement of control surfaces.
- Landing Gear: Supporting the wheels and various articulation points.
- Engine Accessories: Used in auxiliary power units (APUs), pumps, and generators.
- Aircraft Actuators: Facilitating the movement of flaps, slats, and other components.
- Spacecraft Components: Used in satellite mechanisms and other space-grade applications where reliability in vacuum and extreme temperatures is critical.
Medical Equipment
The medical field requires bearings that offer exceptional precision, quiet operation, and often corrosion resistance, especially in sterile environments. Chinese suppliers provide bearings for:
- Dental Equipment: High-speed dental drills utilize miniature, ultra-precise bearings.
- Surgical Tools: Enabling precise movements in robotic surgery systems and other specialized instruments.
- Diagnostic Imaging Equipment: Used in CT scanners, MRI machines, and X-ray systems for smooth rotational movements.
- Laboratory Equipment: Found in centrifuges, agitators, and pumps, where cleanliness and reliability are essential.
- Infusion Pumps and Syringes: Providing precise and consistent fluid delivery.
Consumer Electronics
The compact size and smooth operation of miniature and small ball bearings make them indispensable in various consumer electronic devices.
- Computer Cooling Fans: Essential for dissipating heat from CPUs and other components, ensuring quiet and efficient operation.
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): Used in the spindle motors to rotate platters at very high speeds with minimal vibration.
- Printers and Scanners: Facilitating the movement of print heads and scanning mechanisms.
- Home Appliances: Found in washing machines, vacuum cleaners, and refrigerators, contributing to their durability and performance.
- Drones: Used in motors and gimbals for stable flight and camera operation.
Robotics
As robotics continues to expand into manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and consumer applications, the demand for specialized bearings grows.
- Joints and Actuators: Enabling precise, articulated movements in robotic arms and manipulators. Bearings must offer high rigidity, low friction, and often minimal backlash.
- Gears and Transmissions: Critical for power transfer and speed reduction within robotic systems.
- Grippers and End Effectors: Facilitating the controlled opening and closing actions.
- Mobile Robots: Supporting wheels and tracks for locomotion.
The broad range of applications underscores China's crucial role in the global supply chain for ball bearings, demonstrating its capacity to produce components that meet the diverse and demanding requirements of modern industries.
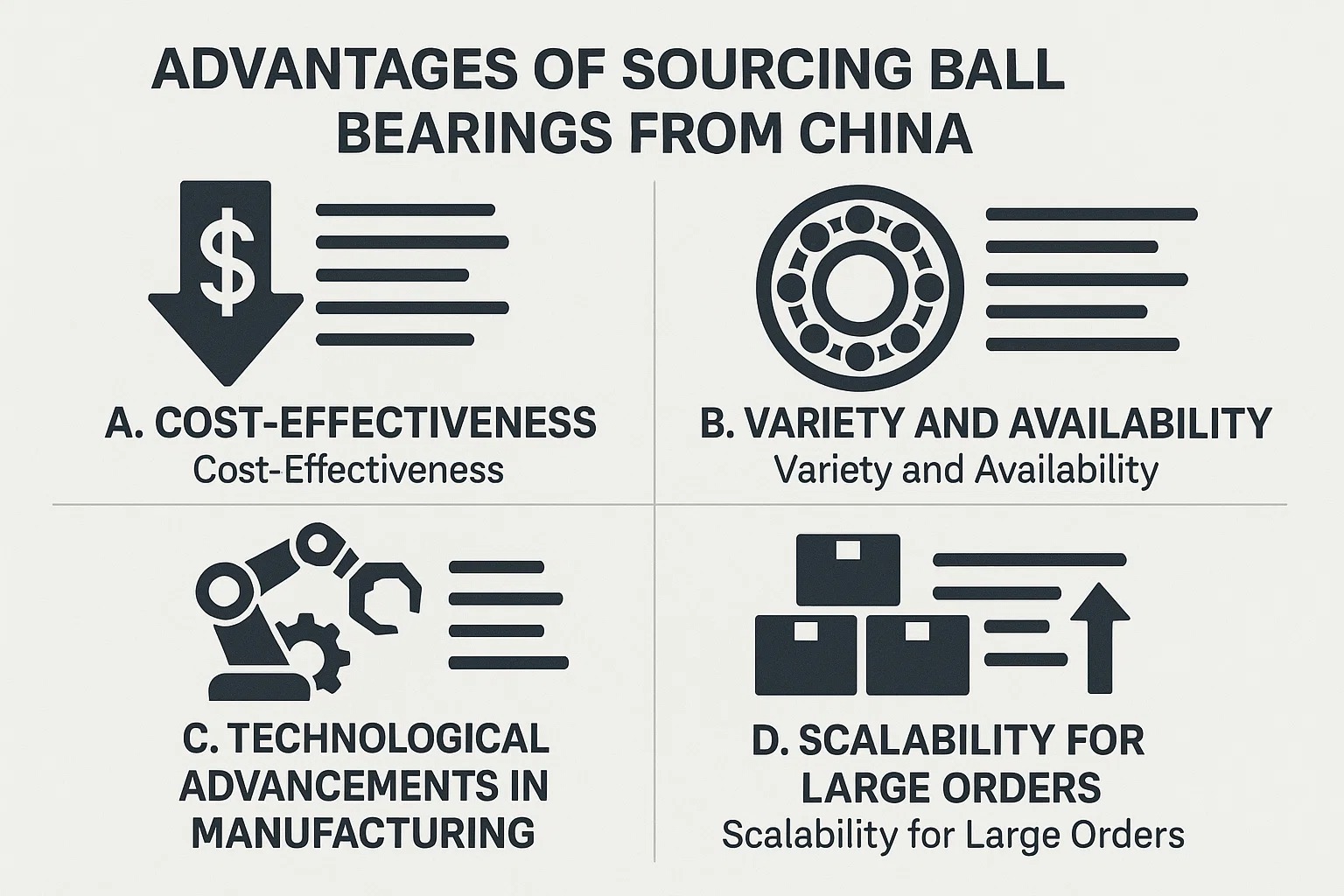
VIII. Advantages of Sourcing Ball Bearings from China
For businesses globally, sourcing ball bearings from China presents a compelling proposition, offering a range of benefits that can significantly impact operational efficiency, cost structures, and supply chain robustness. While quality concerns might have existed in the past, significant advancements mean that these advantages are now coupled with increasingly reliable product performance.
A. Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most immediate and significant advantages of sourcing ball bearings from China is the inherent cost-effectiveness. This is driven by several factors:
Competitive Labor Costs: While rising, labor costs in China remain generally more competitive than in many Western industrialized nations. This directly translates to lower manufacturing overheads for labor-intensive processes.
Economies of Scale: China's vast manufacturing infrastructure and immense production volumes allow for unparalleled economies of scale. Manufacturers can produce bearings in massive quantities, driving down the per-unit cost through optimized production runs, bulk material purchasing, and efficient resource utilization.
Developed Supply Chain Ecosystem: The mature and integrated supply chain for manufacturing within China means that raw materials, specialized components, and ancillary services are readily available and competitively priced. This reduces logistics costs and procurement complexities for bearing manufacturers, which in turn benefits the buyer.
Government Support and Industrial Clusters: Government policies have historically supported the manufacturing sector, and the presence of dedicated industrial clusters for bearing production (e.g., in Linqing, Wafangdian, Cixi) fosters intense competition among local suppliers, driving prices down while encouraging innovation.
These factors collectively contribute to a highly competitive pricing structure for Chinese ball bearings, allowing businesses to optimize their procurement budgets without necessarily compromising on quality, especially for standard and high-volume requirements.
B. Variety and Availability
The sheer breadth of offerings and ready availability of ball bearings from China are unparalleled in the global market.
Extensive Product Range: Chinese manufacturers produce virtually every type of ball bearing imaginable, from standard deep groove and angular contact bearings to highly specialized thin-section, miniature, and custom-designed bearings. This extensive range means that buyers can find suitable bearings for almost any application, regardless of size, load requirement, speed, or environmental conditions.
Customization Capabilities: Beyond standard types, leading Chinese bearing manufacturers possess robust R&D and manufacturing capabilities to produce custom ball bearings tailored to specific client needs. This includes unique dimensions, special materials (e.g., specific stainless steel grades, high-performance ceramics), specialized coatings, and integrated features. This flexibility is crucial for innovative product development and niche applications.
High Production Capacity: China's immense manufacturing capacity ensures that large volumes of bearings can be produced and supplied consistently. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with high demand, preventing bottlenecks in their own production lines.
Ready Stock and Shorter Lead Times: For many standard bearing types, Chinese suppliers often maintain large inventories, facilitating quick turnaround times and reducing lead times, which is critical for just-in-time manufacturing and rapid prototyping.
C. Technological Advancements in Manufacturing
The narrative of Chinese manufacturing has evolved from basic replication to significant innovation. The ball bearing industry reflects this, with continuous investment in advanced technology.
Modern Production Equipment: Leading Chinese bearing factories are equipped with state-of-the-art machinery, including advanced CNC grinding machines, automated assembly lines, precision measurement equipment, and sophisticated heat treatment facilities. This ensures high precision, consistency, and efficiency in production.
Automation and Robotics: As discussed under future trends, the integration of automation and robotics is becoming increasingly prevalent. This not only boosts production capacity but also improves product quality by reducing human error and ensuring tighter control over manufacturing processes.
Material Science and Engineering: Chinese manufacturers are investing heavily in material science research, developing higher-purity steels, advanced ceramics, and specialized coatings that enhance bearing performance, durability, and operational capabilities in extreme environments.
Quality Control Technologies: The adoption of advanced quality control technologies, such as sophisticated optical inspection systems, noise and vibration analysis equipment, and comprehensive metallurgical testing, ensures that bearings meet stringent quality standards before leaving the factory.
Industry 4.0 Integration: Many top-tier manufacturers are embracing Industry 4.0 principles, leveraging IoT, big data analytics, and AI to optimize production processes, enable predictive maintenance of machinery, and enhance overall operational intelligence.
D. Scalability for Large Orders
For global enterprises and large-scale industrial operations, the ability to scale orders seamlessly is a significant advantage, and this is where Chinese ball bearing manufacturers excel.
Mass Production Capabilities: The sheer scale of China's bearing industry means that manufacturers can handle extremely large orders without compromising on delivery schedules or quality. This capacity is critical for industries that require millions of bearings annually.
Flexible Production Planning: Reputable manufacturers can often adjust their production schedules to accommodate fluctuating demands from large clients, providing a level of flexibility that supports dynamic supply chain management.
Consolidated Sourcing: For buyers requiring a diverse range of bearing types in high volumes, China offers a consolidated sourcing solution. This simplifies procurement, reduces administrative overheads, and can lead to stronger, more efficient supplier relationships.
Export Infrastructure: China has a well-developed export infrastructure, including efficient shipping ports, logistics networks, and experience with international trade regulations, making the process of receiving large orders relatively smooth and reliable.
By leveraging these advantages, businesses can establish robust, cost-effective, and high-quality supply chains for their ball bearing needs, supporting their growth and operational efficiency on a global scale.
Conclusion
A. Recap of the Key Points
This guide has explored the multifaceted world of China ball bearings, highlighting their pivotal role across diverse industries. We've traced the remarkable transformation of the Chinese bearing industry from its early stages to its current global dominance, driven by significant advancements in manufacturing capabilities and adherence to international quality standards. We delved into the wide array of ball bearing types produced, from ubiquitous standard bearings to specialized custom and high-performance varieties, emphasizing the crucial role of materials like chrome steel, stainless steel, and advanced ceramics in determining their characteristics. Furthermore, we examined the stringent quality standards (ISO, DIN) and certifications (ISO 9001, IATF 16949) that leading Chinese manufacturers now uphold, alongside their robust quality control measures. Looking ahead, the industry is poised for continued innovation, embracing advanced materials, smart bearing technologies, and Industry 4.0 automation. Finally, we underscored the compelling advantages of sourcing from China, including unparalleled cost-effectiveness, immense product variety and availability, continuous technological advancements, and exceptional scalability for large orders.
B. Final Thoughts on Sourcing Ball Bearings from China
In conclusion, the decision to source ball bearings from China is no longer solely about cost. It is increasingly about leveraging a sophisticated manufacturing ecosystem that offers a compelling combination of competitive pricing, extensive product breadth, and rapidly improving quality and technological prowess. While due diligence remains essential – including thorough supplier vetting, quality auditing, and clear communication of specifications – the opportunities presented by China's ball bearing industry are significant. For businesses seeking reliable, high-performance, and economically viable bearing solutions, China stands as an indispensable and increasingly strategic partner in the global supply chain. By making informed decisions and building strong relationships with reputable Chinese manufacturers, companies can unlock substantial value and enhance their competitive edge.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى









 Download Catalog
Download Catalog
