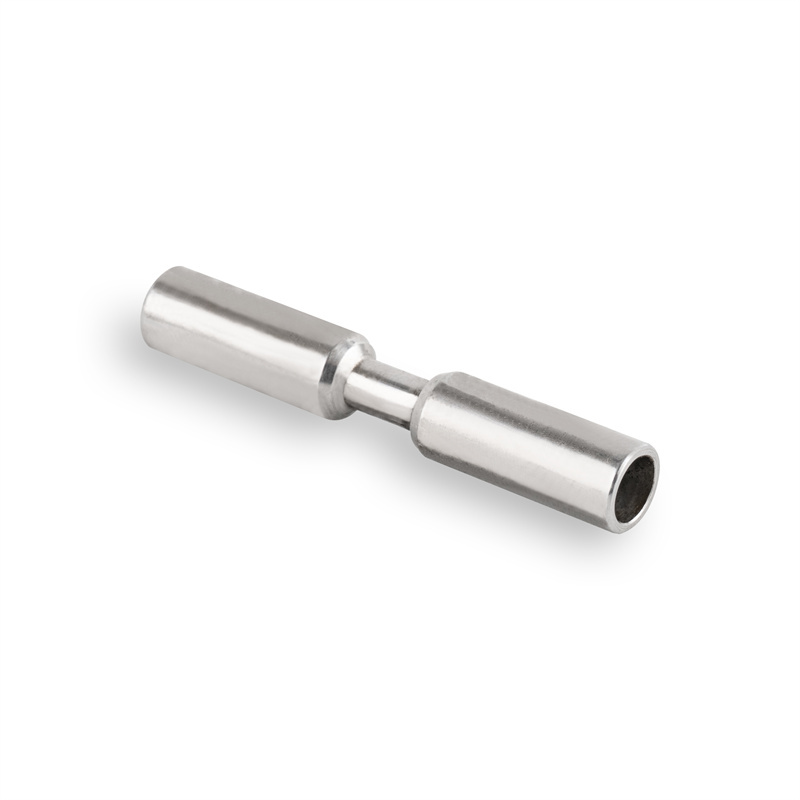
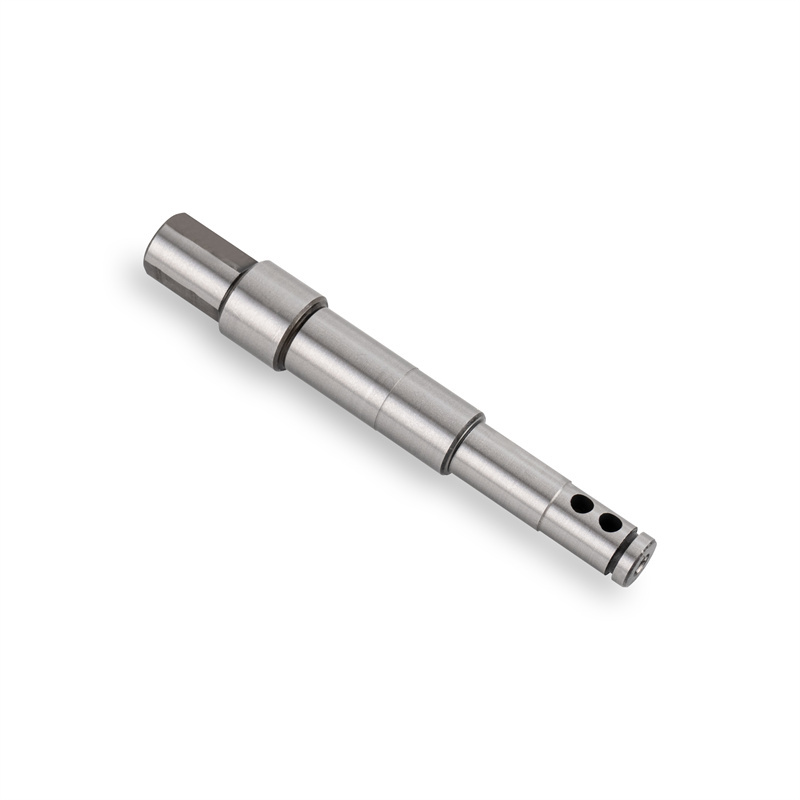
Features of CNC Machined Shafts
High Precision:
CNC machining provides extremely high precision and tight tolerances, typically within a few microns. This ensures that the shaft dimensions meet exact specifications and are consistent across production runs.
Complex Geometries:
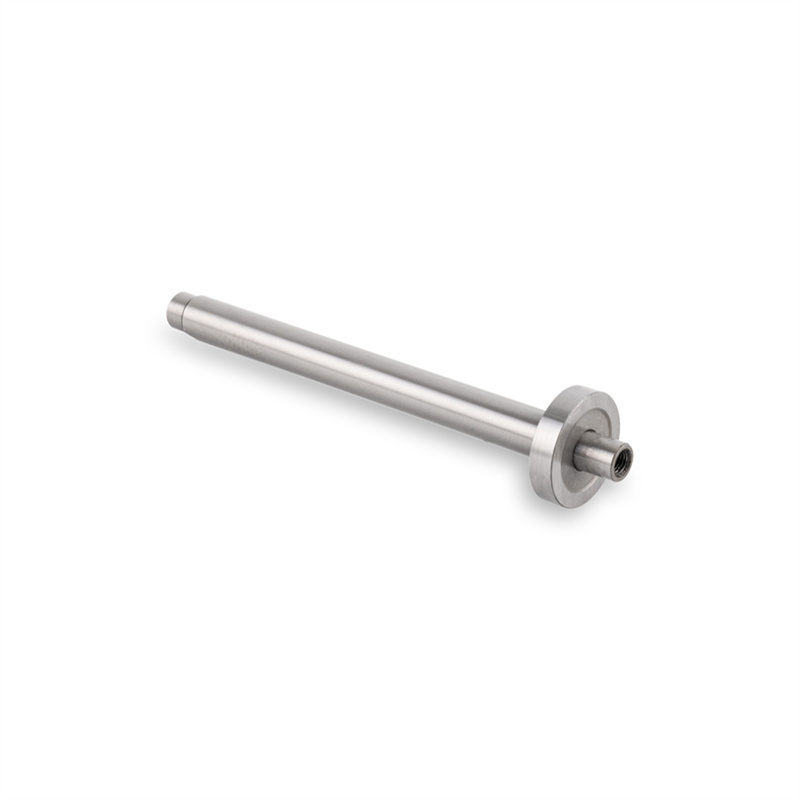
CNC machines can create shafts with intricate features such as grooves, slots, keyways, splines, and tapers, which are often required for specific applications. Multi-axis CNC machines can handle complex shapes and contours.
Surface Finish:
CNC machining provides excellent surface finishes, essential for parts like shafts that interface with other components, such as bearings or seals. Secondary processes like polishing or grinding may also be applied to improve surface quality further.
Heat Treatment and Hardening:
Shafts may undergo heat treatments such as quenching, tempering, or case hardening to increase their strength, hardness, and durability. CNC machining ensures that post-heat treatment dimensions are still within tolerance.
Threading and Holes:
CNC machining can easily add threads to shafts, both internally and externally, and drill precise holes for securing other components or for alignment purposes.
CNC Machining Processes for Shafts
Turning:
CNC turning is used to shape the shaft by rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material. This process is essential for creating cylindrical shapes, including the main shaft body, shoulders, and grooves.
Milling:
CNC milling is used to add complex features to the shaft, such as keyways, flats, or splines. It involves the movement of a rotating cutting tool while the workpiece remains stationary or moves in a controlled manner.
Grinding:
In some cases, shafts require grinding to achieve ultra-smooth surfaces or very tight tolerances. CNC grinding machines are used to finish the shaft after turning and milling processes.
Drilling and Boring:
CNC drilling and boring are used to create precise holes in the shaft for securing it to other components or for reducing weight. Holes may also be tapped or threaded as needed.
Threading:
CNC threading involves cutting internal or external threads on the shaft to allow for the attachment of nuts, bolts, or other threaded components.
Types of CNC Machined Shafts
Transmission Shafts:
Used in automotive and industrial applications to transmit power between different components. These shafts must be able to withstand high torque and load conditions.
Spindle Shafts:
These are high-precision shafts used in machine tools like lathes and milling machines. They require extremely tight tolerances and surface finishes to ensure the accurate rotation of cutting tools.
Rotary Shafts:
These shafts are designed to rotate and support motion in machines such as motors, pumps, and conveyors.
Stepped Shafts:
Shafts that have different diameters along their length are often used for positioning or interfacing with multiple components.
Spline Shafts:
Shafts with spline teeth along their length are used to transfer torque between the shaft and mating parts like gears or hubs.
Keyed Shafts:
Shafts with keyways cut into them are used to fit into matching slots in gears or pulleys, providing a positive drive connection.
Applications of CNC Machined Shafts
Automotive Industry:
CNC-machined shafts are used in engines, transmissions, and drive systems, such as crankshafts, camshafts, and drive shafts. Precision is crucial for ensuring proper vehicle performance and efficiency.
Aerospace:
Aerospace applications require lightweight yet strong shafts that meet extremely tight tolerances. CNC-machined shafts are used in jet engines, landing gear systems, and rotor assemblies.
Industrial Machinery:
Shafts are used in equipment such as conveyors, motors, pumps, and gearboxes. CNC machining ensures the durability and accuracy needed for reliable industrial performance.
Medical Devices:
Precision CNC machined shafts are found in medical equipment, such as surgical robots and diagnostic machines, where exact movements and reliability are essential.
Robotics:
Shafts are critical components in robots, where precision movement and torque transmission are necessary for robotic arms and other motion systems.
Advantages of CNC Machined Shafts
- Precision: CNC machines offer high accuracy and consistency, making them ideal for producing shafts with exacting specifications.
- Efficiency: CNC machining is faster and more efficient for mass production or small batches, ensuring shorter lead times.
- Customization: CNC machining allows for custom designs and shapes, making it suitable for specialized shafts with complex geometries.
- High Repeatability: CNC processes ensure that each machined shaft meets the same exact specifications, providing consistency across production runs.
CNC machined shafts are critical components in a wide range of industries due to their precision, strength, and versatility. The ability to machine shafts with high accuracy and complex features makes CNC machining an essential process for producing high-quality shafts used in everything from automotive engines to industrial machinery.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى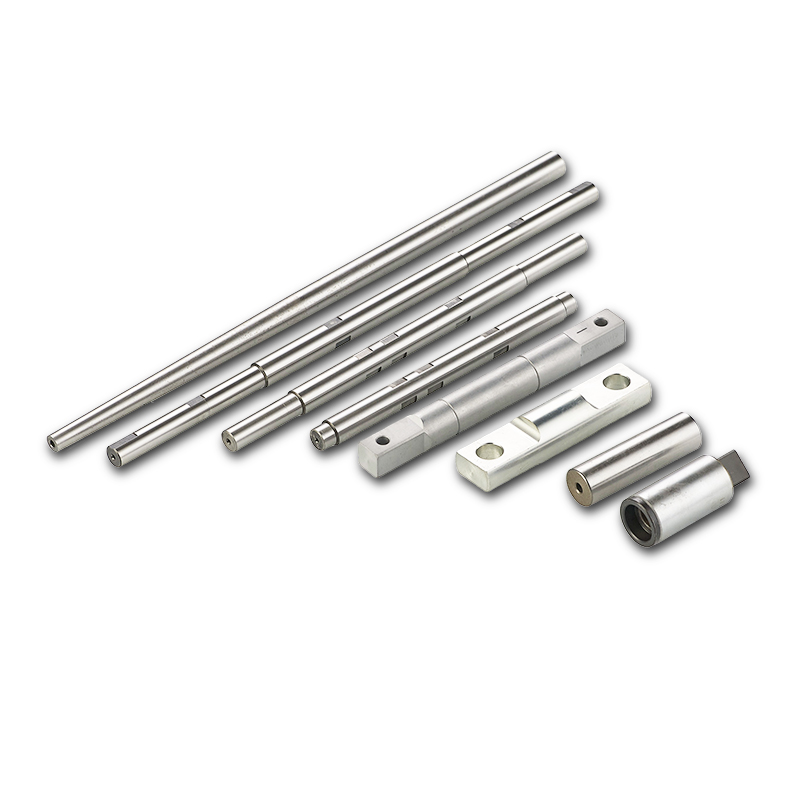




















 Download Catalog
Download Catalog
